Modules
Modules are the most inclusive and generally used addon type. Inside the modules folder, directory structure is almost identical to a Laravel project with one exception which is the src is used instead of app:
catalog
|-- database
|-- migrations
|-- resources
|-- routes
|-- src
|-- Console
|-- Resources
+-- CatalogModule.php
+-- CatalogModuleServiceProvider.php
|-- tests
|-- Catalog
+-- CatalogTest.php
+-- TestCase.php
+-- composer.json
+-- phpunit.xml.dist
Creating a Module
By saying creating we mean to create the necessary files and folders for our module addon. Before diving into addon creation, we must note that every addon we create must have a unique name throughout the application.
Having said that, let's create the catalog module of our e-commerce application using bazaar as vendor and catalog as the unique addon name:
php artisan make:module bazaar.catalog
This would create the following files and folders:
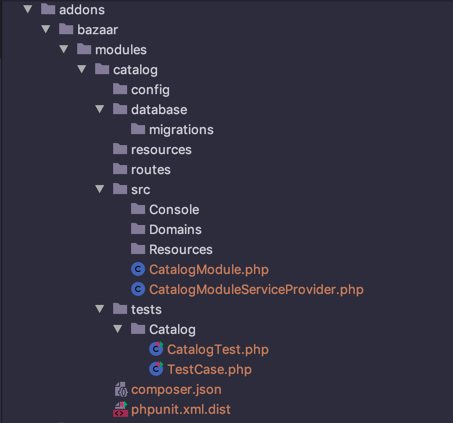
And here's composer.json file created, with type parameter superv-module indicating that this is a special type of composer package.
{
"name": "bazaar/catalog",
"type": "superv-module",
"autoload": {
"psr-4": {
"Bazaar\\Modules\\Catalog\\": "src/"
}
},
"autoload-dev": {
"psr-4": {
"Tests\\": "tests"
}
},
"require": {
"superv/platform": "*"
}
}
Installing a Module
Addons must be installed in order to boot along with the superV platform:
php artisan addon:install addons/bazaar/modules/catalog
When installing an addon, the innstaller will run all the migrations located in your addon's database/migrations folder.
While developing an addon, you can tweak your migrations then run addon:reinstall command to uninstall and install again. And also addon:uninstall to just uninstall to completely remove it.
← Introduction Panels →